Provisions & FAQs – E-Invoicing under GST
E-Invoicing
The Government of India has made E-invoicing compulsory for taxpayers having turnover greater than Rs.500 Cr w.e.f. 1st October, 2020 vide N/No. 61/2020 – CT dated 30th July, 2020. Further, another notification namely, N/No. 88/2020 – CT dated 10th November, 2020, has made E-Invoicing compulsory for taxpayers having turnover greater than Rs.100 Cr w.e.f. 1st January, 2020.
Since, e-invoicing provisions are now applicable to taxpayers having turnover greater than Rs.100 Cr w.e.f. 1st January 2020, therefore, a huge number of companies are falling under the bracket. Further, the e-invoicing compliance is such a continuous and a day-by-day process, it has caused a lot of confusion and commotion among the taxpayers.
We are explaining various provision related to E-invoicing as per our interpretation of Rules and Regulation..
What is E-invoicing?
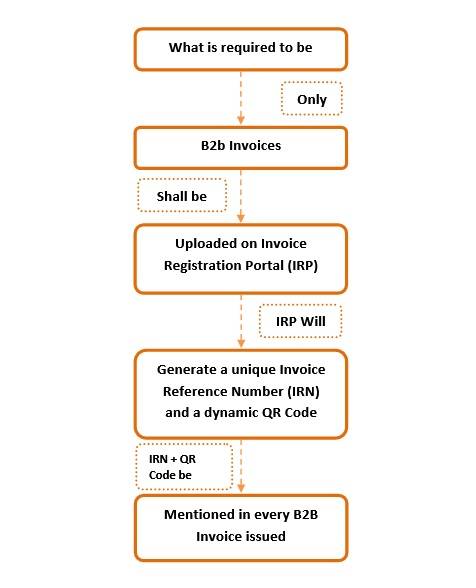
Electronic Invoicing is an electronic authentication mechanism under GST. Under the mechanism, all the B2B invoices generated by a business will have to be authenticated on the GSTN portal, electronically. Furthermore, to manage these invoices, the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) will issue a unique identification number for every invoice called as Invoice Reference Number (IRN)
.
| Myth | Reality |
| A process wherein invoices are to be generated online. | A process wherein invoices already generated in your accounting software are to be authenticated online. |
Further, to understand the compliance better, hereunder is a flowchart to describe the basic procedure to be followed on a daily basis:
What are the benefits of E-Invoicing?
- Reducing the risk tax leakage, frauds and fake invoicing
- One-time reporting of the invoicing details for all your GST filings
- Minimized invoice mismatches during GSTR-2A reconciliation
- Real-time tracking of invoices prepared by the supplier
- Automated return filing process as necessary details shall be auto-populated for various returns and even EWB (Part A)
- Easy and Precise ITC claim
Who all are exempted from the provisions of E-invoicing?
The following are exempted from the provisions of E-invoicing:
- An Insurer, Banking Company, or Financial Institution including NBFC
- Admission to the exhibition of Cinematograph Films in Multiplex Screens
- Goods Transport Agency (GTA)
- Passenger Transport Service
- SEZ Unit
What is the time limit of generating an E-Invoice?
There has been no time-limit prescribed for authentication of E-Invoice. However, Rule 48(5) states that any invoice issued by a person, on whom provisions of e-invoicing is applicable, other than an e-invoice shall be invalid. Therefore, if the recipient wants to claim the input tax credit then, he shall have a valid invoice [as per Sec 16(2)(a)], i.e., e-invoice. Further, if the supply involves movement of goods and the EWB is not accompanied with a valid invoice then the goods are liable for confiscation. Thus, the specified person shall generate the e-invoice before making it available to the recipients.
How can an e-invoice be modified/cancelled?
Correction or modification of any e-invoice is not allowed. However, if any taxpayer wishes to modify the data/figures already mentioned in the e-invoice, then he/she shall cancel the same and generate a new e-invoice.
Further, any e-invoice can be only cancelled within 24 hours of its generation.
Any cancellation done after 24 hours of an E-invoice generation cannot be reported to the IRN portal. In such cases, the taxpayer will have to manually update/cancel the invoice on the GST portal before the returns are filed.
Deceived convenience of E-Invoicing
E-invoicing seems like a lot of work and a lot of compliance work. Further, there seems no point of another compliance work when there is already monthly return filing. However, with e-invoicing comes a deceived convenience which mostly everyone overlooks. The GST mechanism has been designed as such that once an e-invoice is generated, the invoices are pushed to the GST Portal. Thereby, meaning that the Table 4 (All B2B supplies) of GSTR-1 would be auto-filled on a real-time basis. This would largely reduce the monthly compliance burden.
| Condition | Effect on GSTR-1 |
| Invoice modified in GSTR-1 | If e-invoice details are edited by the taxpayer directly in the GSTR-1, then IRN and IRN date fields will be reset to blank |
| E-Invoice cancelled | Such details will be deleted in the respective tables |
| Updation of details in GSTR-1 | Taxpayers can update additional details other than auto-populated from IRP |
Furthermore, another option has been provided on the IRP to push the data in bulk to the E-Way Bill portal, wherein, IRN-wise invoices along with their delivery details are to be mentioned in a excel offline utility. A JSON file shall be created after validation of the excel offline utility. Once the JSON file is uploaded to the IRP successfully, the details of the particular invoices shall be pushed to the EWB portal.
Therefore, it may be said that e-invoicing has increased the compliance burden of the taxpayer, but in reality, we are embracing automation and getting into simplified return filing in totality. Just imagine , by a single click in the ERP of the taxpayer, an invoice for outward supply gets authenticated on the IRP, gets published in GSTR-1 and an EWB is also generated on a real time-basis. This is the deceived convenience of e-invoicing.
FAQs:
Q. What documents are presently covered under e-invoicing?
i. Invoices
ii. Credit Notes
iii. Debit Notes,
when issued by notified class of taxpayers (to registered persons (B2B) or for the purpose of Exports) are currently covered under e-invoice.
Though different documents are covered, for ease of reference and understanding, the system is referred as ‘e-invoicing’.
Q. What supplies are presently covered under e-invoice?
Supplies to registered persons (B2B), Supplies to SEZs (with/without payment), Exports (with/without payment), Deemed Exports, by notified class of taxpayers are currently covered under e-invoicing.
Q. B2C (Business to Consumer) supplies can also be reported by notified persons?
No. Reporting B2C invoices by notified persons is not applicable/allowed currently. However, they will be brought under e-invoice in the next phase.
Q. Is e-invoicing applicable for NIL-rated or wholly-exempt supplies?
No. In those cases, a bill of supply is issued and not a tax invoice.
Q. Whether the financial/commercial credit notes also need to be reported to IRP?
No, only the credit and debit notes issued under Section 34 of CGST/SGST Act have to be reported.
Q. Whether e-invoicing is applicable for invoices between two different GSTINs under same PAN?
Yes. e-invoicing by notified persons is mandated for supply of goods or services or both to a registered person.
As per Section 25(4) of CGST/SGST Act, “A person who has obtained or is required to obtain more than one registration, whether in one State or Union territory or more than one State or Union territory shall, in respect of each such registration, be treated as distinct persons for the purposes of this Act.”
Q. What is the applicability of e-invoice for import transactions?
E-invoicing is not applicable for import Bills of Entry.
Q. Do SEZ Developers need to issue e-invoices?
Yes, if they have the specified turnover and fulfilling other conditions of the notification.
In terms of Notification (Central Tax) 61/2020 dt. 30-7-2020, only SEZ Units are exempted from issuing e-invoices.
Q. Whether e-invoicing is applicable for supplies involving Reverse Charge?
If the invoice issued by notified person is in respect of supplies made by him but attracting reverse charge under Section 9(3), e-invoicing is applicable.
For example, a taxpayer (say, a Firm of Advocates having aggregate turnover in a FY is more than Rs. 500 Cr.) is supplying services to a company (who will be discharging tax liability as recipient under RCM), such invoices have to be reported by the notified person to IRP. On the other hand, where supplies are received by notified person from (i) an unregistered person (attracting reverse charge under Section 9(4)) or (ii) through import of services, e-invoicing doesn’t arise / not applicable.
Q. Do I need to print QR Code on the invoice? If so, what shall be its size and location on the invoice copy?
Yes. The QR code (containing, inter alia, the IRN) which comes as part of signed JSON from IRP, shall be extracted and printed on the invoice. This is one of the mandatory particulars of invoice under Rule 46 of CGST Rules. While the printed QR code shall be clear enough to be readable by a QR Code reader, the size and its placing on invoice is upto the preference of the businesses.
Q. While returning IRN, the IRP is also adding its digital signature, “Acknowledgement No.” and “Date”. Whether these also need to be printed while issuing invoice?
No. There is no mandate to print these particulars on invoice copy. Note that the “Acknowledgement No.” and “Date” given by IRP are only for reference. Being a 15-digit number, the acknowledgement number will also come handy for printing e-invoice or for generating e-way bill (instead of keying in the 64-character long IRN).
Q. If e-invoice is applicable and issued, am I supposed to issue copies of invoice in triplicate/duplicate?
Where e-invoicing is applicable, there is no need of issuing invoice copies in triplicate/duplicate. This is clearly specified in Rule 48(6).
Starting at just Rs 499*
You might be interested in:
Union Budget 2021 – All The Changes Announced!
Is Supply of Goods a Taxable Event Under GST Law ?
New Grounds For Cancellation of Registration under GST
Critical Mistakes to Look For After GST Registration!
Whether Late Filing Fees (Interest u/s 234A) is Applicable For F.Y 2019-20?

